Quick Answer: How Do You Determine Fair Market Value of Inherited Property?
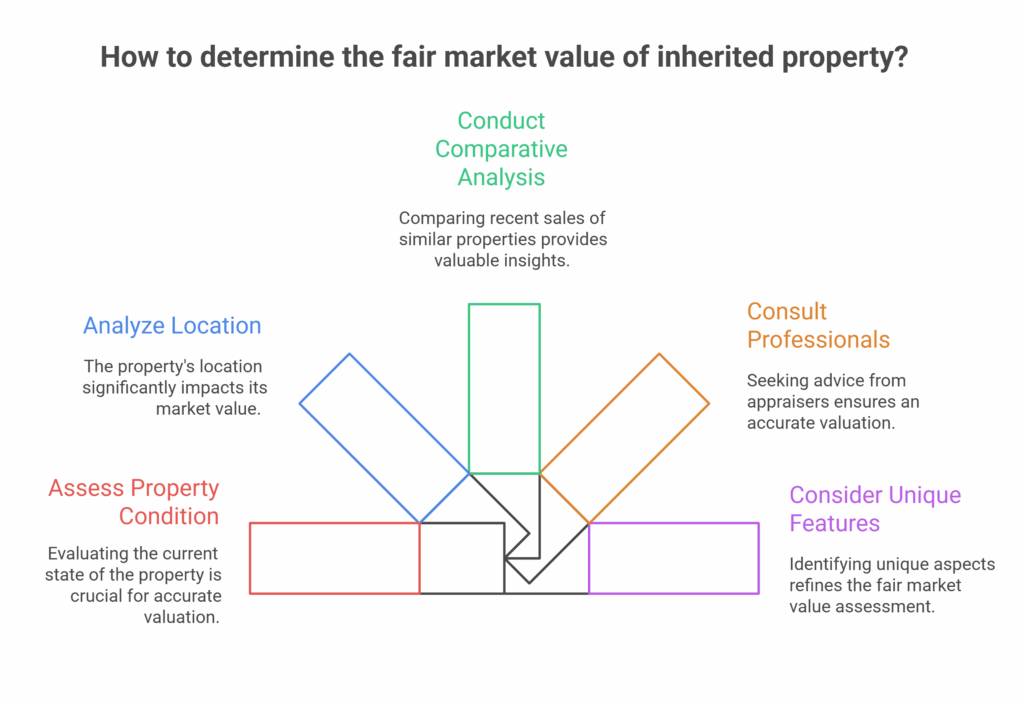
How Do You Determine Fair Market Value Of Inherited Property? The process usually involves getting a professional appraisal, comparing recent sales of similar properties in the area, and reviewing tax assessments or market trends. Executors often rely on a certified appraiser to provide an accurate valuation that meets legal and IRS requirements.
This fair market value is essential for probate, tax reporting, and making informed decisions about whether to sell, rent, or retain the inherited property.
Now let’s dive deeper.
Why Fair Market Value Matters for Taxes?
When you inherit property, its fair market value (FMV) is crucial to know not only for consideration of whether to sell or retain it but also for tax reasons. Most heirs have no idea of the potential tax consequences involved in inherited real property, which makes it even more important to know FMV correctly. But how do you determine fair market value of inherited property by tax guidelines? This blog discusses the place of FMV in tax evaluation, possible liabilities, and methods of reducing tax charges.
Fair market value is the approximate price at which a property is exchanged on an open market in normal circumstances. Taxing bodies like the IRS apply that fair market valuation to levy estate taxes, capital gains taxes, and other financial charges related to the passing of inheritance of the property. The FMV when the decedent dies sets the new cost basis for the property in question, which is quite important from a tax reporting perspective.
Estate Tax Considerations
For estates above federal or state exemption levels, estate taxes can be levied. FMV is an important factor in calculating the total taxable value of the estate. If the total value of an estate—plus the property inherited—is above the federal exemption level ($13.61 million in 2024), heirs might have to pay estate taxes. States with their estate taxes might have varying exemption levels.
Capital Gains Tax and the Stepped-Up Basis Rule
One of the major tax advantages of inherited assets is the stepped-up basis rule. Instead of inheriting the original cost basis, heirs receive a stepped-up basis to the FMV at the time of death. This is beneficial to them since capital gains tax only applies to gains realized upon the sale of the asset for a price higher than its adjusted basis.
For example, The original price at which the property was bought is now $200,000, but the fair market value when inherited was $500,000; hence, the new cost basis for the heir is $500,000. After selling it for $550,000, they will also pay capital gains tax just over the profit of $50,000 and not over $350,000.
Tax Reporting and FMV Determination Methods
Tax reporting requires an accurate valuation of inherited property, and there are several accepted methods for establishing FMV:
- Professional Appraisals: Hiring a licensed real estate appraiser is the most widely accepted method, particularly for tax purposes. The appraiser assesses the market conditions, comparable sales, and property attributes to arrive at a fair valuation.
- Comparable Sale Analysis: A study of the latest sales of properties comparable to the subject property can yield FMV. Tax professionals use this method with appraisal reports.
- Tax Assessment Records: Local tax assessment records can give clues, but they are not necessarily a correct indicator of FMV, as assessed values are usually below market prices.
- Real Estate Agent Comparative Market Analysis (CMA): A CMA from a local real estate agent provides an estimate based on recent sales and current listings but is not as formal as an official appraisal.
Ways to Minimize Tax Liabilities
- Hold the Property: If conditions in the market are poor, holding the property for some time can minimize possible capital gains exposure when selling afterward.
- Apply the Primary Residence Exclusion: If the beneficiary lives in the inherited home for two years before selling, they may be able to claim an exclusion of up to $250,000 (up to $500,000 for couples) on the capital gain.
- Consider a 1031 Exchange: In case of selling the property inherited and re-investing in some other property, a 1031 exchange might delay capital gains taxes.
- Make Strategic Improvements: Certain improvements can raise the adjusted cost basis, lowering taxable gains upon sale.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Relying on Outdated Valuations: The FMV should reflect the market at the time of inheritance, not old appraisals or tax records.
- Ignoring Professional Advice: Consulting with a tax professional can prevent costly mistakes in tax filings and potential audits.
- Selling Without Understanding Tax Consequences: Selling too soon without considering stepped-up basis advantages could lead to unnecessary tax payments.
It’s important to understand how you determine the fair market value of inherited property for fair market value accurately for appropriate tax reporting and reducing potential financial liability. Because valuations affect everything from estate taxes to any capital gains implications, obtaining the right valuation will ensure that you are compliant and able to save. If you missed our previous blog post on different valuation methods to determine FMV, be sure to read it for a holistic understanding of the process before getting into tax implications. It will help you choose the right approach to valuation, setting the stage for informed financial decisions.
Final Thoughts
Determining the fair market value of inherited property is essential for making informed financial decisions, whether you’re handling taxes, planning to sell, or navigating estate settlements. Understanding FMV helps you avoid unnecessary tax liabilities and ensures you get the best value when selling.
If you’re looking for a hassle-free way to sell your inherited property, we’re here to help. At Move On House Buyers, we buy houses in El Paso, Texas, for cash—regardless of their condition. No need to worry about costly repairs, financing delays, or complicated paperwork. We handle everything and can close in as little as seven days. Let us take the stress off your shoulders and provide you with a fair, no-obligation cash offer today!
Call us anytime at 713-561-5162 or connect with us on our website and we’ll lay out all of your options for your specific situation.
